What Type Of Bond Is Formed Between Amino Acids
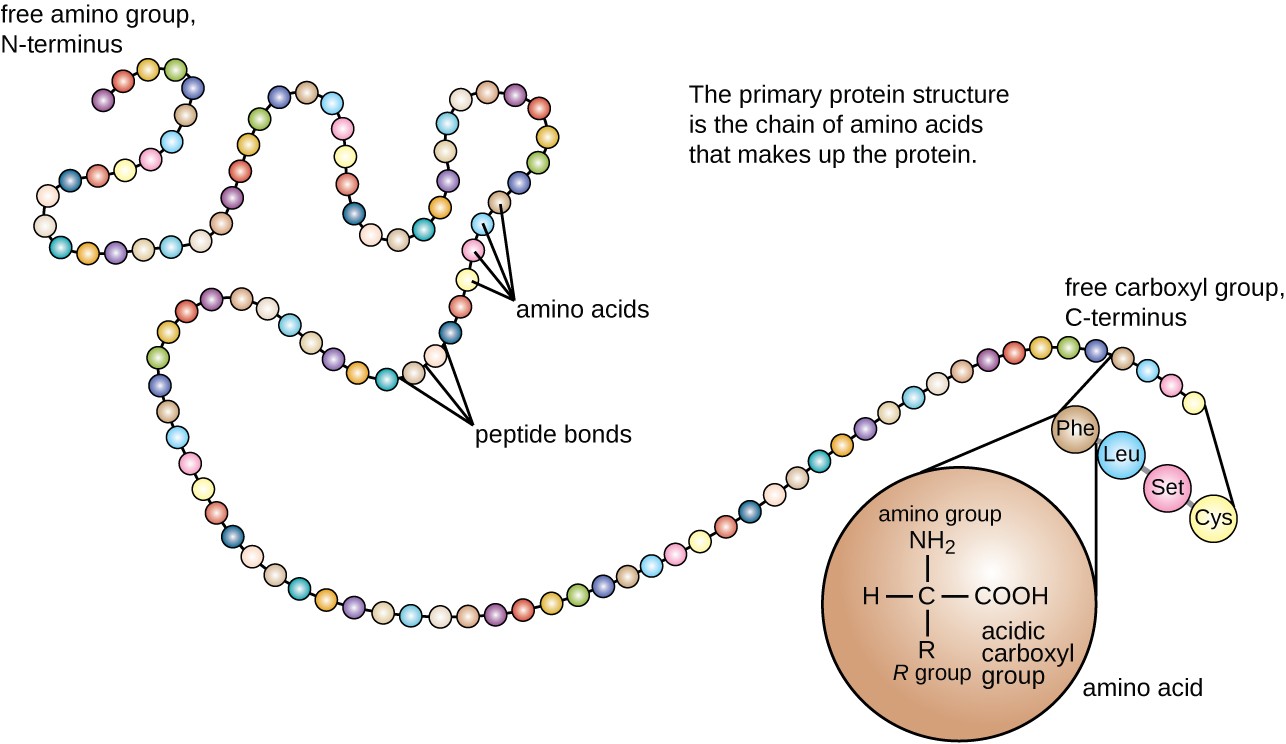
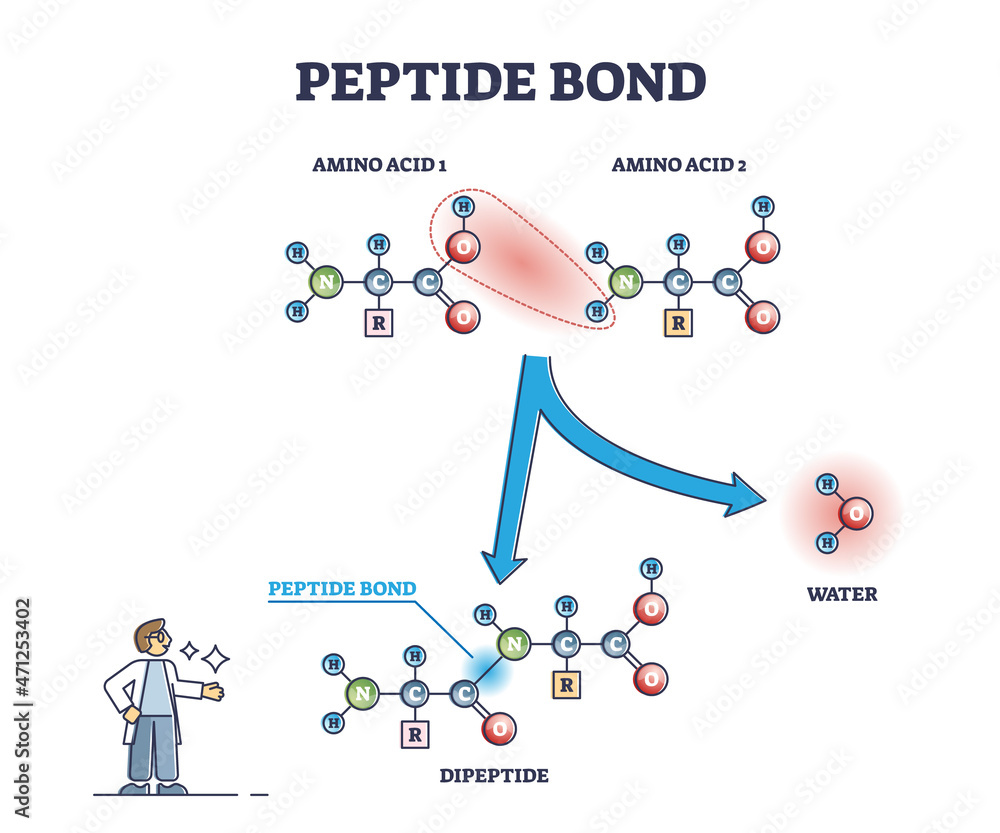
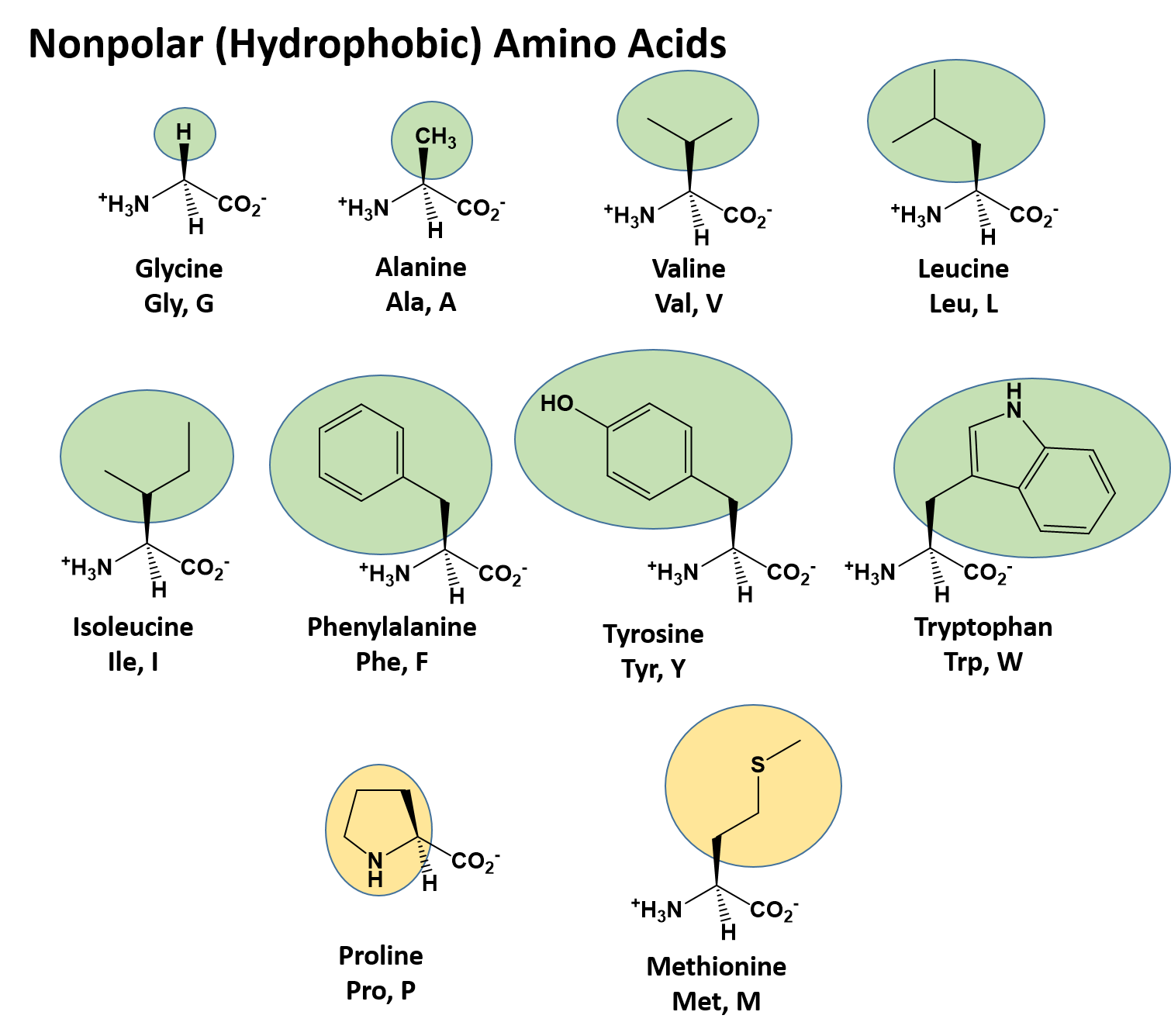
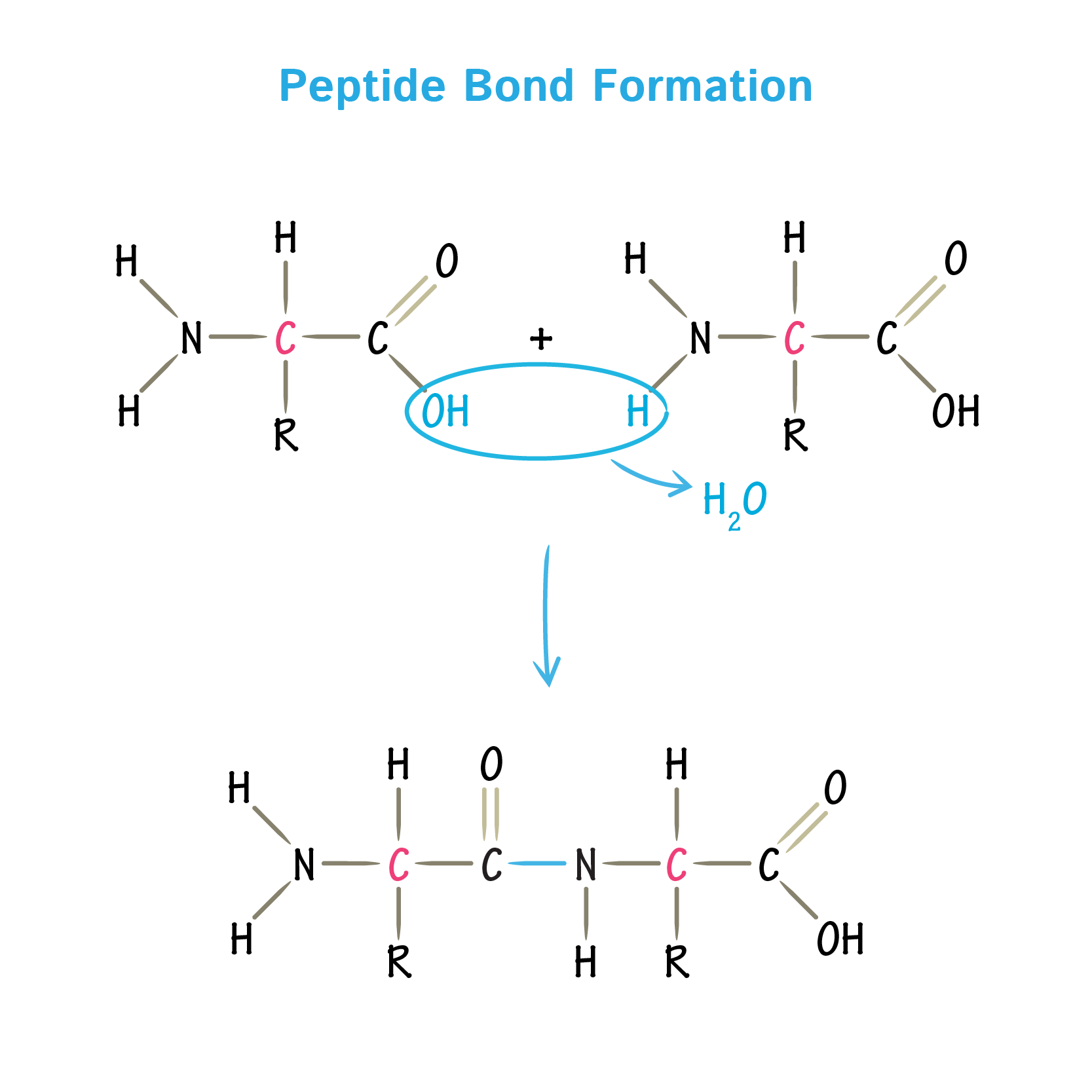
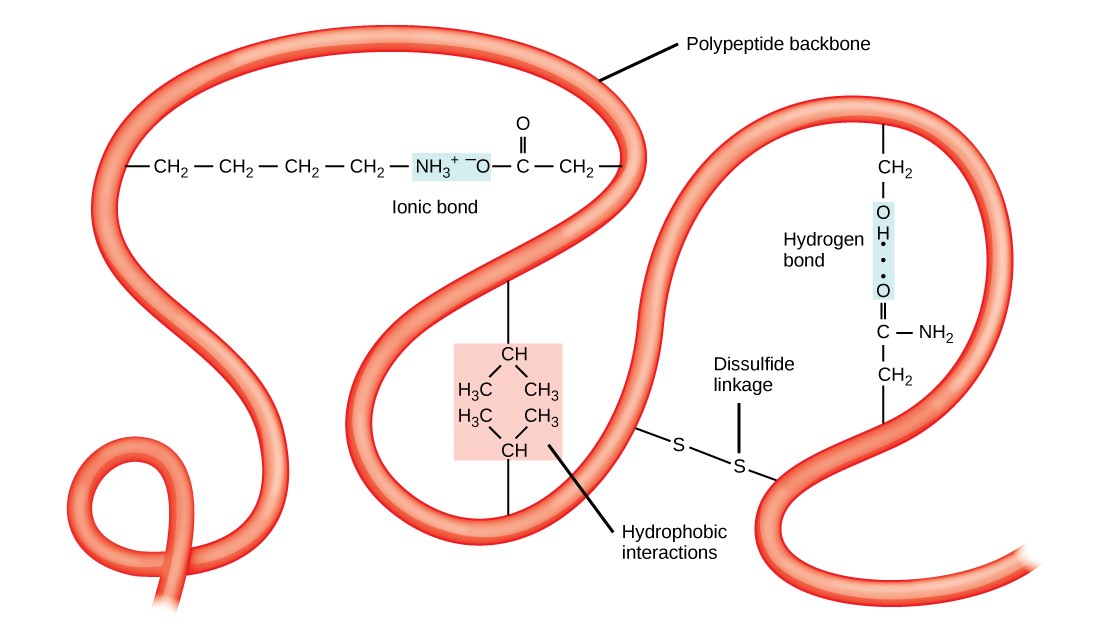
What Type Of Bond Is Formed Between Amino Acids - Each amino acid has the same core structure, which consists of a central carbon atom, also known as the alpha (α) carbon, bonded to an amino group (nh2),. You will be expected to. Other intramolecular bonds that stabilize the folding processes include. Hydrogen bonds stabilize the folding occurrences. Amino acids are bonded together by covalent peptide bonds to form a dipeptide in a condensation reaction.
Amino acids are bonded together by covalent peptide bonds to form a dipeptide in a condensation reaction. You will be expected to. Other intramolecular bonds that stabilize the folding processes include. Each amino acid has the same core structure, which consists of a central carbon atom, also known as the alpha (α) carbon, bonded to an amino group (nh2),. Hydrogen bonds stabilize the folding occurrences.
Other intramolecular bonds that stabilize the folding processes include. You will be expected to. Amino acids are bonded together by covalent peptide bonds to form a dipeptide in a condensation reaction. Hydrogen bonds stabilize the folding occurrences. Each amino acid has the same core structure, which consists of a central carbon atom, also known as the alpha (α) carbon, bonded to an amino group (nh2),.
How do you Identify a Peptide Bond?
Hydrogen bonds stabilize the folding occurrences. Each amino acid has the same core structure, which consists of a central carbon atom, also known as the alpha (α) carbon, bonded to an amino group (nh2),. Amino acids are bonded together by covalent peptide bonds to form a dipeptide in a condensation reaction. Other intramolecular bonds that stabilize the folding processes include..
Proteins Microbiology
Amino acids are bonded together by covalent peptide bonds to form a dipeptide in a condensation reaction. Hydrogen bonds stabilize the folding occurrences. Each amino acid has the same core structure, which consists of a central carbon atom, also known as the alpha (α) carbon, bonded to an amino group (nh2),. Other intramolecular bonds that stabilize the folding processes include..
Protéine, Acide aminé, Peptide Définition simple et complète Espace
You will be expected to. Each amino acid has the same core structure, which consists of a central carbon atom, also known as the alpha (α) carbon, bonded to an amino group (nh2),. Hydrogen bonds stabilize the folding occurrences. Other intramolecular bonds that stabilize the folding processes include. Amino acids are bonded together by covalent peptide bonds to form a.
Obraz Peptide bond as amino acids formation in protein biosynthesis
Other intramolecular bonds that stabilize the folding processes include. Each amino acid has the same core structure, which consists of a central carbon atom, also known as the alpha (α) carbon, bonded to an amino group (nh2),. You will be expected to. Amino acids are bonded together by covalent peptide bonds to form a dipeptide in a condensation reaction. Hydrogen.
Structure of Amino Acids and Proteins
Hydrogen bonds stabilize the folding occurrences. Each amino acid has the same core structure, which consists of a central carbon atom, also known as the alpha (α) carbon, bonded to an amino group (nh2),. Other intramolecular bonds that stabilize the folding processes include. You will be expected to. Amino acids are bonded together by covalent peptide bonds to form a.
Chapter 2 Protein Structure Chemistry
You will be expected to. Hydrogen bonds stabilize the folding occurrences. Each amino acid has the same core structure, which consists of a central carbon atom, also known as the alpha (α) carbon, bonded to an amino group (nh2),. Amino acids are bonded together by covalent peptide bonds to form a dipeptide in a condensation reaction. Other intramolecular bonds that.
Amino acids physical, chemical properties and peptide bond
Other intramolecular bonds that stabilize the folding processes include. Amino acids are bonded together by covalent peptide bonds to form a dipeptide in a condensation reaction. You will be expected to. Hydrogen bonds stabilize the folding occurrences. Each amino acid has the same core structure, which consists of a central carbon atom, also known as the alpha (α) carbon, bonded.
Chapter 3. Amino Acids & Proteins Introduction to Molecular and Cell
Hydrogen bonds stabilize the folding occurrences. Each amino acid has the same core structure, which consists of a central carbon atom, also known as the alpha (α) carbon, bonded to an amino group (nh2),. Amino acids are bonded together by covalent peptide bonds to form a dipeptide in a condensation reaction. You will be expected to. Other intramolecular bonds that.
Amino Acids Structure Nutrition
Each amino acid has the same core structure, which consists of a central carbon atom, also known as the alpha (α) carbon, bonded to an amino group (nh2),. Amino acids are bonded together by covalent peptide bonds to form a dipeptide in a condensation reaction. Hydrogen bonds stabilize the folding occurrences. You will be expected to. Other intramolecular bonds that.
This figure shows the secondary structure of peptides. The top panel
You will be expected to. Amino acids are bonded together by covalent peptide bonds to form a dipeptide in a condensation reaction. Each amino acid has the same core structure, which consists of a central carbon atom, also known as the alpha (α) carbon, bonded to an amino group (nh2),. Hydrogen bonds stabilize the folding occurrences. Other intramolecular bonds that.
Hydrogen Bonds Stabilize The Folding Occurrences.
Amino acids are bonded together by covalent peptide bonds to form a dipeptide in a condensation reaction. You will be expected to. Each amino acid has the same core structure, which consists of a central carbon atom, also known as the alpha (α) carbon, bonded to an amino group (nh2),. Other intramolecular bonds that stabilize the folding processes include.