Selection Bias Definition
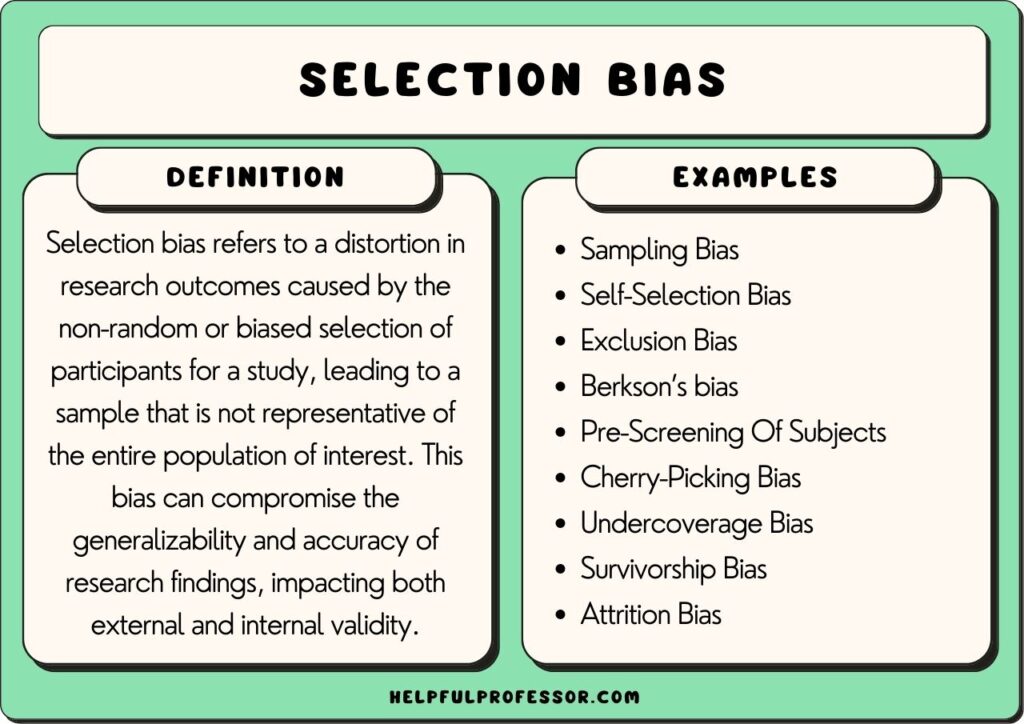
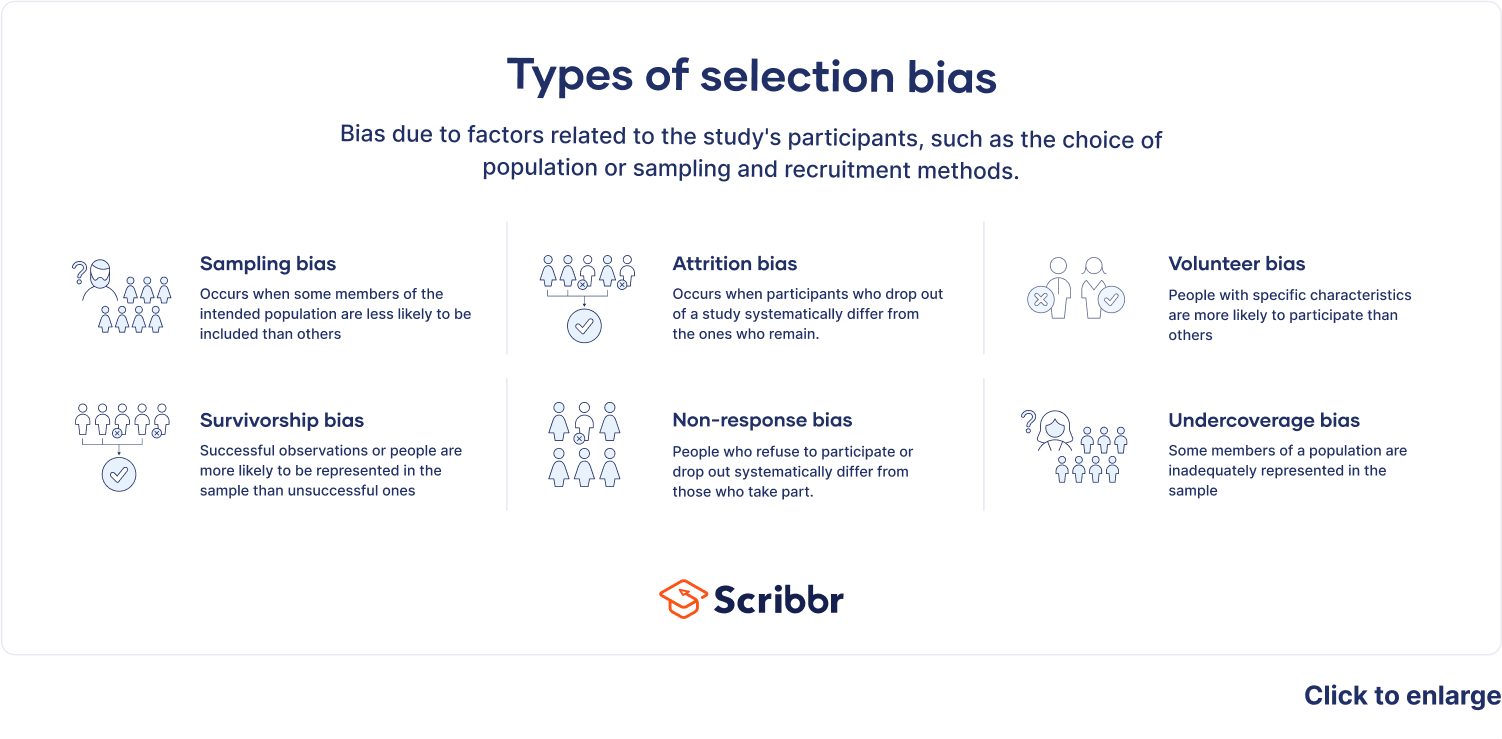
Selection Bias Definition - Selection bias is the bias introduced by the selection of individuals, groups, or data for analysis in such a way that proper randomization is not achieved, thereby failing to ensure that the sample obtained. The selection of individuals or groups in a study. Selection bias occurs where the sampling method for an rct does not produce truly random allocation between the treatments being compared. Understanding the different types of selection bias can help researchers identify potential sources of. Selection bias is a critical issue that can affect the accuracy and reliability of research findings. Selection bias is a general term describing errors arising from factors related to the population being studied, but there are several types of selection bias:
Selection bias is a critical issue that can affect the accuracy and reliability of research findings. The selection of individuals or groups in a study. Selection bias occurs where the sampling method for an rct does not produce truly random allocation between the treatments being compared. Selection bias is the bias introduced by the selection of individuals, groups, or data for analysis in such a way that proper randomization is not achieved, thereby failing to ensure that the sample obtained. Selection bias is a general term describing errors arising from factors related to the population being studied, but there are several types of selection bias: Understanding the different types of selection bias can help researchers identify potential sources of.
The selection of individuals or groups in a study. Selection bias is the bias introduced by the selection of individuals, groups, or data for analysis in such a way that proper randomization is not achieved, thereby failing to ensure that the sample obtained. Selection bias is a critical issue that can affect the accuracy and reliability of research findings. Selection bias occurs where the sampling method for an rct does not produce truly random allocation between the treatments being compared. Understanding the different types of selection bias can help researchers identify potential sources of. Selection bias is a general term describing errors arising from factors related to the population being studied, but there are several types of selection bias:
5 Which of the Following Describes Selection Bias LeonidashasDominguez
Selection bias occurs where the sampling method for an rct does not produce truly random allocation between the treatments being compared. Selection bias is the bias introduced by the selection of individuals, groups, or data for analysis in such a way that proper randomization is not achieved, thereby failing to ensure that the sample obtained. The selection of individuals or.
16 Selection Bias Examples (2024)
The selection of individuals or groups in a study. Understanding the different types of selection bias can help researchers identify potential sources of. Selection bias is a critical issue that can affect the accuracy and reliability of research findings. Selection bias is the bias introduced by the selection of individuals, groups, or data for analysis in such a way that.
Biases in Screening test Also selection / Spectrum bias
Selection bias occurs where the sampling method for an rct does not produce truly random allocation between the treatments being compared. Selection bias is a critical issue that can affect the accuracy and reliability of research findings. Understanding the different types of selection bias can help researchers identify potential sources of. Selection bias is the bias introduced by the selection.
10 Selection Bias R for Epidemiology
Selection bias is a critical issue that can affect the accuracy and reliability of research findings. Selection bias is a general term describing errors arising from factors related to the population being studied, but there are several types of selection bias: Understanding the different types of selection bias can help researchers identify potential sources of. Selection bias occurs where the.
Ways to avoid Interviewer bias in your selection process
Selection bias is the bias introduced by the selection of individuals, groups, or data for analysis in such a way that proper randomization is not achieved, thereby failing to ensure that the sample obtained. Understanding the different types of selection bias can help researchers identify potential sources of. The selection of individuals or groups in a study. Selection bias is.
Selection Bias In Research Definition, Types & Examples
Selection bias is a critical issue that can affect the accuracy and reliability of research findings. Selection bias is a general term describing errors arising from factors related to the population being studied, but there are several types of selection bias: Understanding the different types of selection bias can help researchers identify potential sources of. Selection bias is the bias.
Understanding Selection Bias Definition, Types, and Examples
Understanding the different types of selection bias can help researchers identify potential sources of. Selection bias is a general term describing errors arising from factors related to the population being studied, but there are several types of selection bias: The selection of individuals or groups in a study. Selection bias is the bias introduced by the selection of individuals, groups,.
PPT Lecture 8 Selection Bias, Matching, & Control Selection
Selection bias is a general term describing errors arising from factors related to the population being studied, but there are several types of selection bias: The selection of individuals or groups in a study. Selection bias is a critical issue that can affect the accuracy and reliability of research findings. Selection bias occurs where the sampling method for an rct.
What Is Selection Bias? Definition & Examples
Selection bias occurs where the sampling method for an rct does not produce truly random allocation between the treatments being compared. Selection bias is a general term describing errors arising from factors related to the population being studied, but there are several types of selection bias: Selection bias is a critical issue that can affect the accuracy and reliability of.
What is Selection Bias? Andrea Hardy, RD
Selection bias occurs where the sampling method for an rct does not produce truly random allocation between the treatments being compared. The selection of individuals or groups in a study. Selection bias is the bias introduced by the selection of individuals, groups, or data for analysis in such a way that proper randomization is not achieved, thereby failing to ensure.
The Selection Of Individuals Or Groups In A Study.
Selection bias is a critical issue that can affect the accuracy and reliability of research findings. Selection bias is the bias introduced by the selection of individuals, groups, or data for analysis in such a way that proper randomization is not achieved, thereby failing to ensure that the sample obtained. Selection bias occurs where the sampling method for an rct does not produce truly random allocation between the treatments being compared. Understanding the different types of selection bias can help researchers identify potential sources of.