Real And Inverted Image Is Formed By Which Lens
Real And Inverted Image Is Formed By Which Lens - Convex (converging) lenses can form either real or virtual images (cases 1 and 2, respectively), whereas concave (diverging) lenses can form only. For convex lenses, depending on the object's location relative to the lens's focal points and optical center, the image can vary from real and inverted. If a luminous object is placed at a distance greater than the focal length away from a convex lens, then it will form an inverted real.
For convex lenses, depending on the object's location relative to the lens's focal points and optical center, the image can vary from real and inverted. If a luminous object is placed at a distance greater than the focal length away from a convex lens, then it will form an inverted real. Convex (converging) lenses can form either real or virtual images (cases 1 and 2, respectively), whereas concave (diverging) lenses can form only.
For convex lenses, depending on the object's location relative to the lens's focal points and optical center, the image can vary from real and inverted. Convex (converging) lenses can form either real or virtual images (cases 1 and 2, respectively), whereas concave (diverging) lenses can form only. If a luminous object is placed at a distance greater than the focal length away from a convex lens, then it will form an inverted real.
The above image shows a thin lens of focal length 5m. What is the kind
If a luminous object is placed at a distance greater than the focal length away from a convex lens, then it will form an inverted real. Convex (converging) lenses can form either real or virtual images (cases 1 and 2, respectively), whereas concave (diverging) lenses can form only. For convex lenses, depending on the object's location relative to the lens's.
A convex lens forms a real, inverted and same sized image as the object
If a luminous object is placed at a distance greater than the focal length away from a convex lens, then it will form an inverted real. For convex lenses, depending on the object's location relative to the lens's focal points and optical center, the image can vary from real and inverted. Convex (converging) lenses can form either real or virtual.
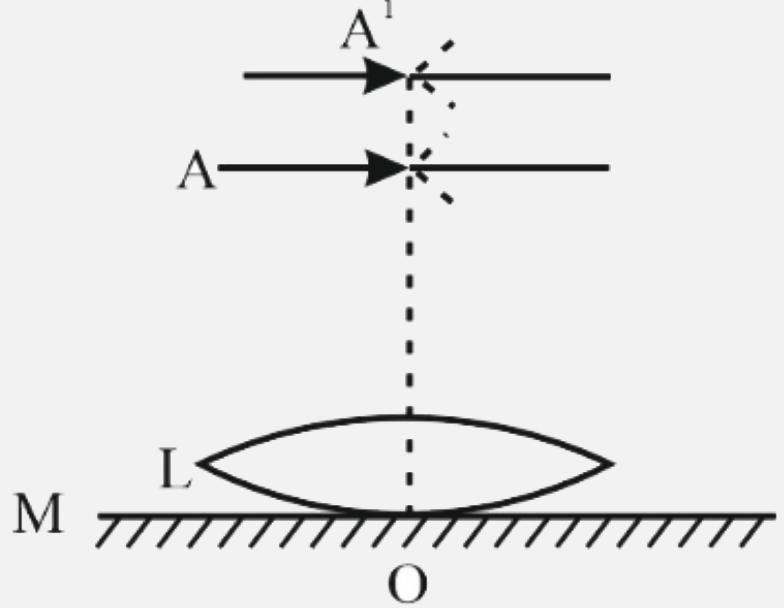
A thin convex lens L (refractive index = 1.5) is placed on a plane mir
Convex (converging) lenses can form either real or virtual images (cases 1 and 2, respectively), whereas concave (diverging) lenses can form only. For convex lenses, depending on the object's location relative to the lens's focal points and optical center, the image can vary from real and inverted. If a luminous object is placed at a distance greater than the focal.
An object is placed 15 cm in front of a lens 'a' and lens gives real
Convex (converging) lenses can form either real or virtual images (cases 1 and 2, respectively), whereas concave (diverging) lenses can form only. If a luminous object is placed at a distance greater than the focal length away from a convex lens, then it will form an inverted real. For convex lenses, depending on the object's location relative to the lens's.
Q2 Page 184 A convex lens forms a real and inverted image of needle
For convex lenses, depending on the object's location relative to the lens's focal points and optical center, the image can vary from real and inverted. Convex (converging) lenses can form either real or virtual images (cases 1 and 2, respectively), whereas concave (diverging) lenses can form only. If a luminous object is placed at a distance greater than the focal.
Why Does A Concave Mirror Invert An Image Mirror Ideas
For convex lenses, depending on the object's location relative to the lens's focal points and optical center, the image can vary from real and inverted. If a luminous object is placed at a distance greater than the focal length away from a convex lens, then it will form an inverted real. Convex (converging) lenses can form either real or virtual.
Image Formation by Lenses Physics
Convex (converging) lenses can form either real or virtual images (cases 1 and 2, respectively), whereas concave (diverging) lenses can form only. For convex lenses, depending on the object's location relative to the lens's focal points and optical center, the image can vary from real and inverted. If a luminous object is placed at a distance greater than the focal.
get a real and inverted image of same size as that of the object by a
If a luminous object is placed at a distance greater than the focal length away from a convex lens, then it will form an inverted real. Convex (converging) lenses can form either real or virtual images (cases 1 and 2, respectively), whereas concave (diverging) lenses can form only. For convex lenses, depending on the object's location relative to the lens's.
Diverging= SUV (small, upright, virtual) image regardless if it's a
For convex lenses, depending on the object's location relative to the lens's focal points and optical center, the image can vary from real and inverted. Convex (converging) lenses can form either real or virtual images (cases 1 and 2, respectively), whereas concave (diverging) lenses can form only. If a luminous object is placed at a distance greater than the focal.
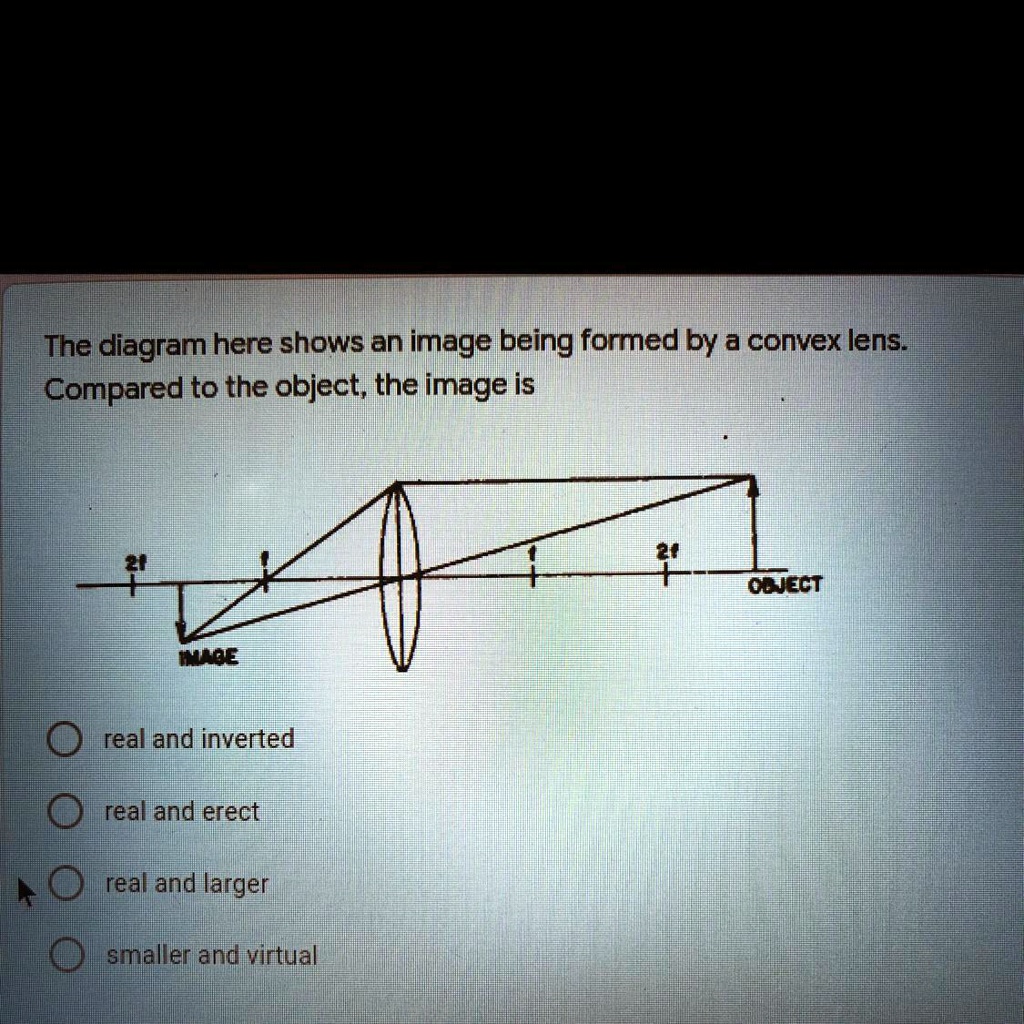
SOLVED The diagram here shows an image being formed by a convex lens
For convex lenses, depending on the object's location relative to the lens's focal points and optical center, the image can vary from real and inverted. Convex (converging) lenses can form either real or virtual images (cases 1 and 2, respectively), whereas concave (diverging) lenses can form only. If a luminous object is placed at a distance greater than the focal.
For Convex Lenses, Depending On The Object's Location Relative To The Lens's Focal Points And Optical Center, The Image Can Vary From Real And Inverted.
If a luminous object is placed at a distance greater than the focal length away from a convex lens, then it will form an inverted real. Convex (converging) lenses can form either real or virtual images (cases 1 and 2, respectively), whereas concave (diverging) lenses can form only.