Normal Range Of Bacteria In Urine During Pregnancy
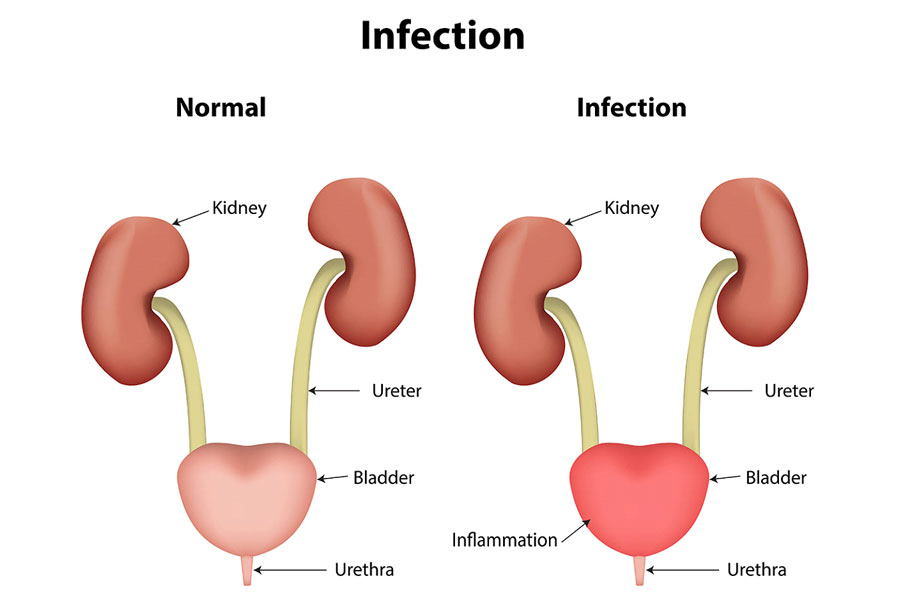
Normal Range Of Bacteria In Urine During Pregnancy - In the normal state of health of a pregnant woman, the urinary fluid is always. Asymptomatic bacteriuria affects 1 to 5 percent of healthy premenopausal women and 1.9 to 9.5 percent of pregnant women. During pregnancy, the likelihood of infection increases due to dilation of the ureter, which leads to decreased urine flow and consequent. The norm of bacteria in urine during pregnancy.
In the normal state of health of a pregnant woman, the urinary fluid is always. Asymptomatic bacteriuria affects 1 to 5 percent of healthy premenopausal women and 1.9 to 9.5 percent of pregnant women. During pregnancy, the likelihood of infection increases due to dilation of the ureter, which leads to decreased urine flow and consequent. The norm of bacteria in urine during pregnancy.
During pregnancy, the likelihood of infection increases due to dilation of the ureter, which leads to decreased urine flow and consequent. Asymptomatic bacteriuria affects 1 to 5 percent of healthy premenopausal women and 1.9 to 9.5 percent of pregnant women. In the normal state of health of a pregnant woman, the urinary fluid is always. The norm of bacteria in urine during pregnancy.
Epithelial Cells in Urine During Pregnancy Types, Normal Ranges & more
In the normal state of health of a pregnant woman, the urinary fluid is always. During pregnancy, the likelihood of infection increases due to dilation of the ureter, which leads to decreased urine flow and consequent. The norm of bacteria in urine during pregnancy. Asymptomatic bacteriuria affects 1 to 5 percent of healthy premenopausal women and 1.9 to 9.5 percent.
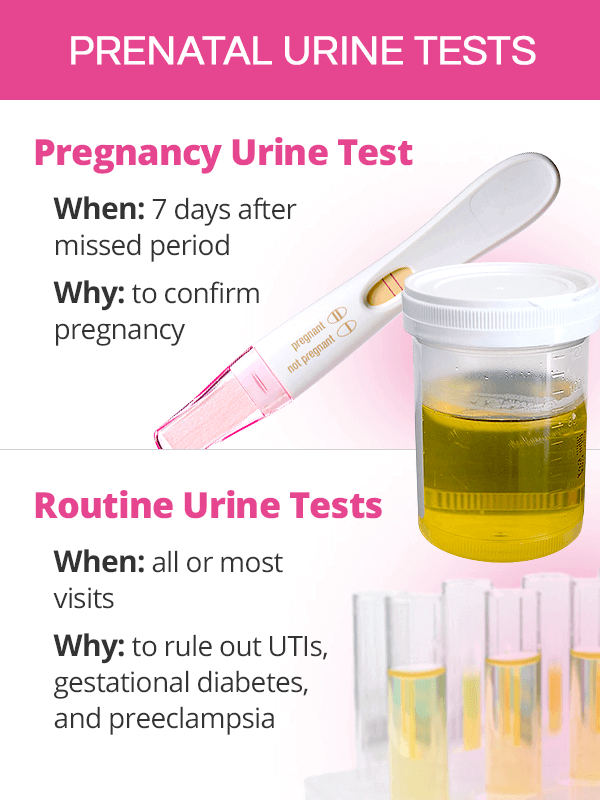
Urine & Blood Tests during Pregnancy SheCares
During pregnancy, the likelihood of infection increases due to dilation of the ureter, which leads to decreased urine flow and consequent. In the normal state of health of a pregnant woman, the urinary fluid is always. Asymptomatic bacteriuria affects 1 to 5 percent of healthy premenopausal women and 1.9 to 9.5 percent of pregnant women. The norm of bacteria in.
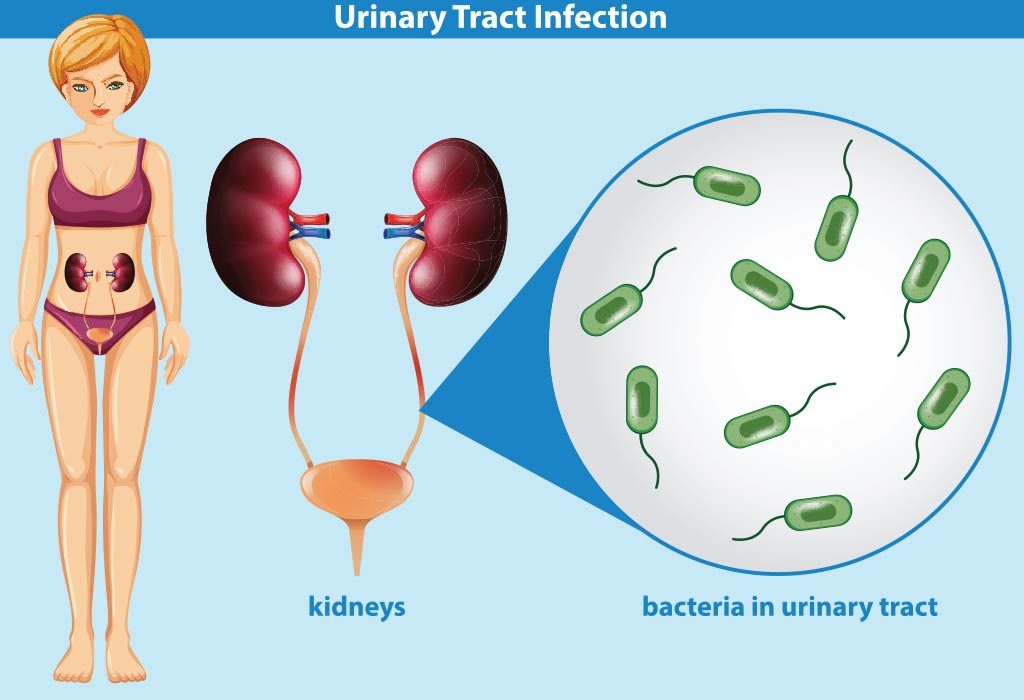
urinary tract infection in women
During pregnancy, the likelihood of infection increases due to dilation of the ureter, which leads to decreased urine flow and consequent. In the normal state of health of a pregnant woman, the urinary fluid is always. The norm of bacteria in urine during pregnancy. Asymptomatic bacteriuria affects 1 to 5 percent of healthy premenopausal women and 1.9 to 9.5 percent.
Causes of urinary tract infection in pregnancy
During pregnancy, the likelihood of infection increases due to dilation of the ureter, which leads to decreased urine flow and consequent. In the normal state of health of a pregnant woman, the urinary fluid is always. The norm of bacteria in urine during pregnancy. Asymptomatic bacteriuria affects 1 to 5 percent of healthy premenopausal women and 1.9 to 9.5 percent.
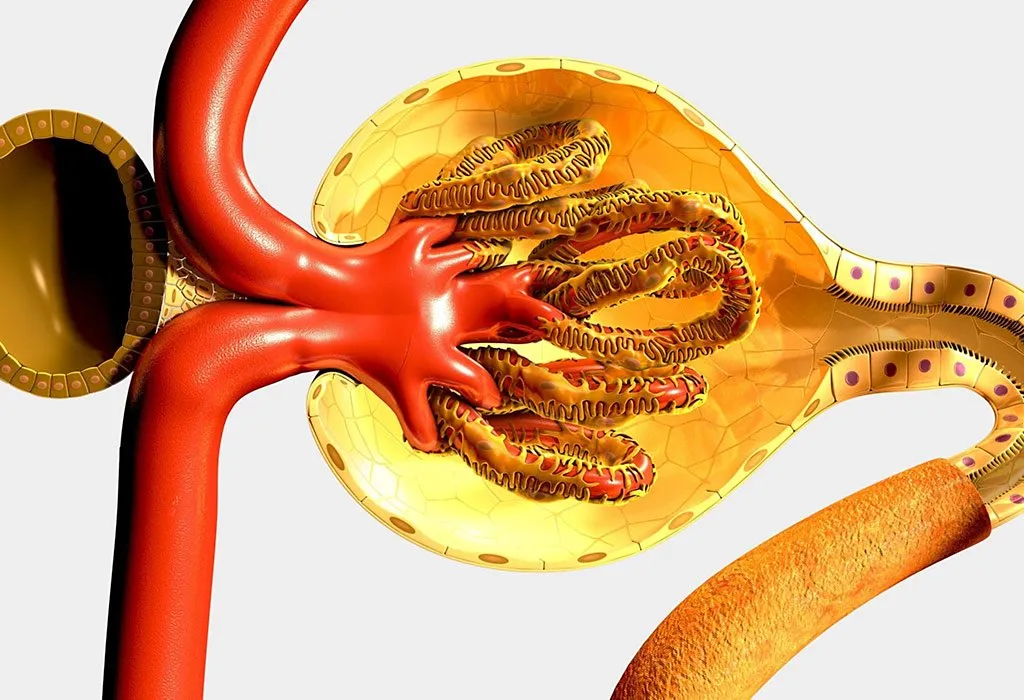
Physiological changes during pregnancy
In the normal state of health of a pregnant woman, the urinary fluid is always. Asymptomatic bacteriuria affects 1 to 5 percent of healthy premenopausal women and 1.9 to 9.5 percent of pregnant women. The norm of bacteria in urine during pregnancy. During pregnancy, the likelihood of infection increases due to dilation of the ureter, which leads to decreased urine.
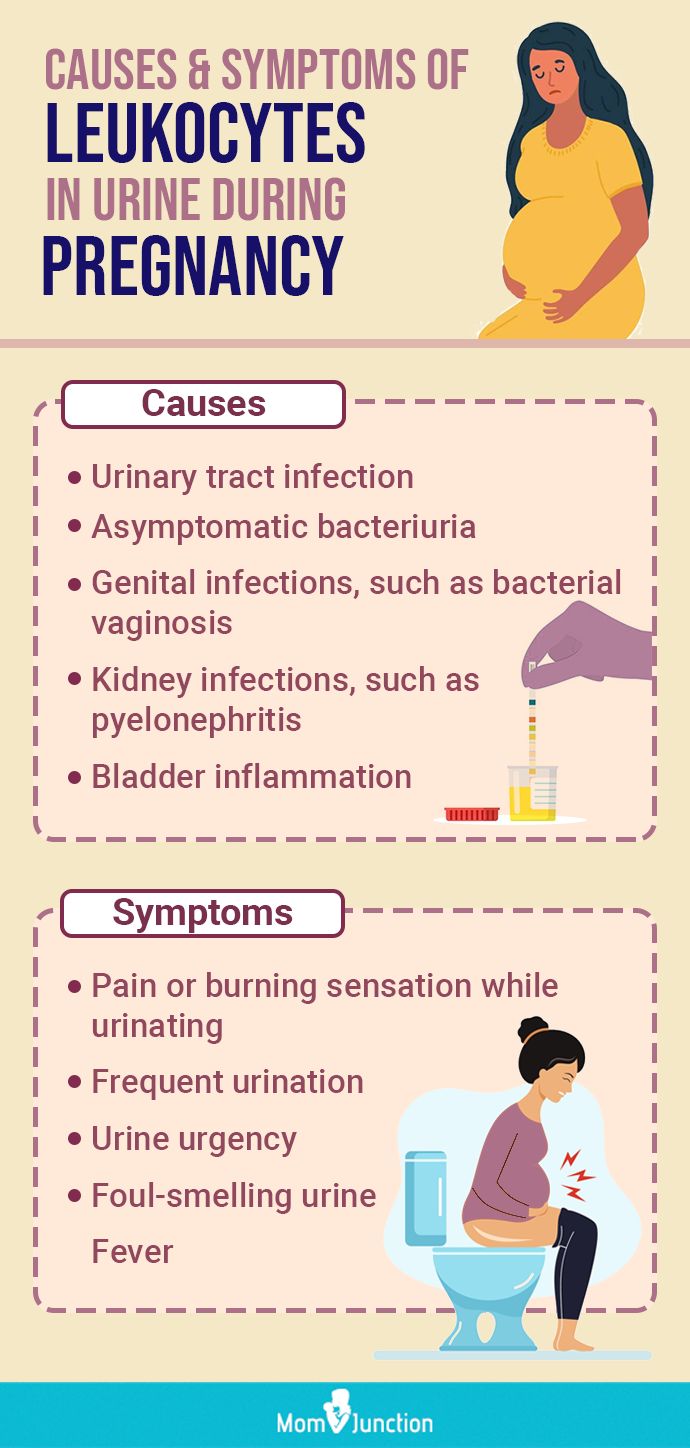
Leukocytes In Urine During Pregnancy Causes And Treatment
In the normal state of health of a pregnant woman, the urinary fluid is always. During pregnancy, the likelihood of infection increases due to dilation of the ureter, which leads to decreased urine flow and consequent. The norm of bacteria in urine during pregnancy. Asymptomatic bacteriuria affects 1 to 5 percent of healthy premenopausal women and 1.9 to 9.5 percent.
Urinary Tract Infection During Pregnancy
Asymptomatic bacteriuria affects 1 to 5 percent of healthy premenopausal women and 1.9 to 9.5 percent of pregnant women. The norm of bacteria in urine during pregnancy. In the normal state of health of a pregnant woman, the urinary fluid is always. During pregnancy, the likelihood of infection increases due to dilation of the ureter, which leads to decreased urine.
Cloudy Urine During Pregnancy [ Infographic]
The norm of bacteria in urine during pregnancy. Asymptomatic bacteriuria affects 1 to 5 percent of healthy premenopausal women and 1.9 to 9.5 percent of pregnant women. During pregnancy, the likelihood of infection increases due to dilation of the ureter, which leads to decreased urine flow and consequent. In the normal state of health of a pregnant woman, the urinary.
Pregnancy Symptoms Urine Infection, Pregnancy Sympthom
During pregnancy, the likelihood of infection increases due to dilation of the ureter, which leads to decreased urine flow and consequent. The norm of bacteria in urine during pregnancy. In the normal state of health of a pregnant woman, the urinary fluid is always. Asymptomatic bacteriuria affects 1 to 5 percent of healthy premenopausal women and 1.9 to 9.5 percent.
Maternal Adaptations in Pregnancy TeachMePhysiology
The norm of bacteria in urine during pregnancy. During pregnancy, the likelihood of infection increases due to dilation of the ureter, which leads to decreased urine flow and consequent. In the normal state of health of a pregnant woman, the urinary fluid is always. Asymptomatic bacteriuria affects 1 to 5 percent of healthy premenopausal women and 1.9 to 9.5 percent.
The Norm Of Bacteria In Urine During Pregnancy.
In the normal state of health of a pregnant woman, the urinary fluid is always. Asymptomatic bacteriuria affects 1 to 5 percent of healthy premenopausal women and 1.9 to 9.5 percent of pregnant women. During pregnancy, the likelihood of infection increases due to dilation of the ureter, which leads to decreased urine flow and consequent.


![Cloudy Urine During Pregnancy [ Infographic]](https://www.findatopdoc.com/var/fatd/storage/images/_aliases/infographic_main/top-videos-and-slideshows/cloudy-urine-during-pregnancy/447315-1-eng-US/Cloudy-Urine-During-Pregnancy.jpg)

