Axiom Math Definition
Axiom Math Definition - It is accepted as true, without proof, as the basis for argument. An axiom serves as the base. An axiom is a statement that is true or assumed to be true without any proof whereas a theorem must be proven. Axioms or postulate is defined as a statement that is accepted as true and correct, called as a theorem in mathematics.
An axiom is a statement that is true or assumed to be true without any proof whereas a theorem must be proven. It is accepted as true, without proof, as the basis for argument. Axioms or postulate is defined as a statement that is accepted as true and correct, called as a theorem in mathematics. An axiom serves as the base.
Axioms or postulate is defined as a statement that is accepted as true and correct, called as a theorem in mathematics. An axiom serves as the base. It is accepted as true, without proof, as the basis for argument. An axiom is a statement that is true or assumed to be true without any proof whereas a theorem must be proven.
Discrete Mathematics Chapter 1 Logic and proofs 1282020
An axiom is a statement that is true or assumed to be true without any proof whereas a theorem must be proven. An axiom serves as the base. It is accepted as true, without proof, as the basis for argument. Axioms or postulate is defined as a statement that is accepted as true and correct, called as a theorem in.
What is an axiom?
Axioms or postulate is defined as a statement that is accepted as true and correct, called as a theorem in mathematics. An axiom is a statement that is true or assumed to be true without any proof whereas a theorem must be proven. It is accepted as true, without proof, as the basis for argument. An axiom serves as the.
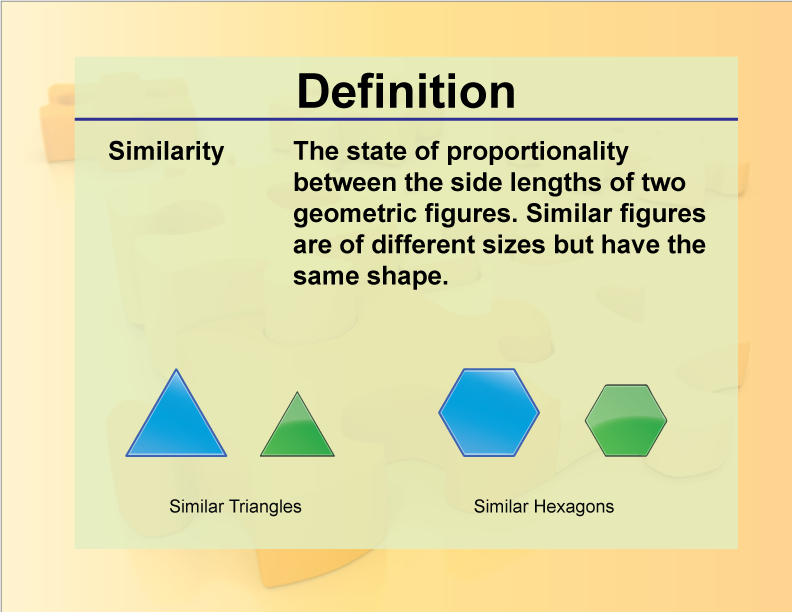
DefinitionGeometry BasicsSimilarity Media4Math
It is accepted as true, without proof, as the basis for argument. Axioms or postulate is defined as a statement that is accepted as true and correct, called as a theorem in mathematics. An axiom serves as the base. An axiom is a statement that is true or assumed to be true without any proof whereas a theorem must be.
PPT Axiomatic Systems PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID4520354
It is accepted as true, without proof, as the basis for argument. An axiom is a statement that is true or assumed to be true without any proof whereas a theorem must be proven. Axioms or postulate is defined as a statement that is accepted as true and correct, called as a theorem in mathematics. An axiom serves as the.
Physics; formulated so as to be indubitable and thus forming a final
It is accepted as true, without proof, as the basis for argument. An axiom serves as the base. Axioms or postulate is defined as a statement that is accepted as true and correct, called as a theorem in mathematics. An axiom is a statement that is true or assumed to be true without any proof whereas a theorem must be.
Definition of Axiom YouTube
Axioms or postulate is defined as a statement that is accepted as true and correct, called as a theorem in mathematics. An axiom serves as the base. It is accepted as true, without proof, as the basis for argument. An axiom is a statement that is true or assumed to be true without any proof whereas a theorem must be.
What Are Axioms? YouTube
It is accepted as true, without proof, as the basis for argument. An axiom serves as the base. An axiom is a statement that is true or assumed to be true without any proof whereas a theorem must be proven. Axioms or postulate is defined as a statement that is accepted as true and correct, called as a theorem in.
Solved What axiom can justify this statement 9* (8+5)=(9* 8)+(9* 5
An axiom serves as the base. Axioms or postulate is defined as a statement that is accepted as true and correct, called as a theorem in mathematics. It is accepted as true, without proof, as the basis for argument. An axiom is a statement that is true or assumed to be true without any proof whereas a theorem must be.
What is an axiom?
An axiom is a statement that is true or assumed to be true without any proof whereas a theorem must be proven. It is accepted as true, without proof, as the basis for argument. An axiom serves as the base. Axioms or postulate is defined as a statement that is accepted as true and correct, called as a theorem in.
What is an Axiom Definition of Axiom
An axiom is a statement that is true or assumed to be true without any proof whereas a theorem must be proven. An axiom serves as the base. Axioms or postulate is defined as a statement that is accepted as true and correct, called as a theorem in mathematics. It is accepted as true, without proof, as the basis for.
An Axiom Serves As The Base.
Axioms or postulate is defined as a statement that is accepted as true and correct, called as a theorem in mathematics. An axiom is a statement that is true or assumed to be true without any proof whereas a theorem must be proven. It is accepted as true, without proof, as the basis for argument.